GREASE APPLICATIONS OF BEARINGS
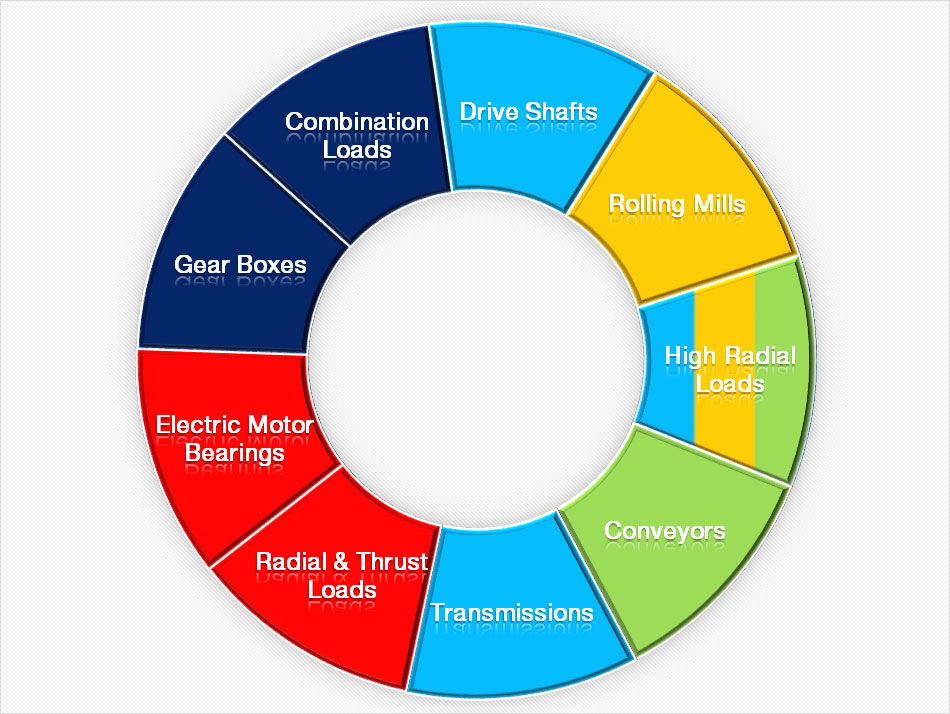
1. Common Applications of Different Types of Bearings

|
:Cylindrical |

|
:Spherical |

|
:Ball |

|
:Needle |

|
:Tapered |
(Ref.: www.skf.com)
2. Bearing Types Affect Grease Life
| Bearing Type | Relative Type of Grease |
|---|---|
| Deep groove, single-row ball bearing | 1 |
| Angular contact, single-row ball bearing | 0.625 |
| Self-aligning ball bearing | 0.77-0.625 |
| Thrust ball bearing | 0.2-0.17 |
| Cylindrical, single-row roller bearing | 0.625-0.43 |
| Needle roller bearing | 0.3 |
| Tapered roller bearing | 0.25 |
| Spherical roller bearing | 0.14-0.08 |
Note: Larger bearings and high speed bearings translate to shorter grease life. High DN grease is required.
(Ref.: Booser, Block, ML)
3. Bearing Under Different Kinds of Loads
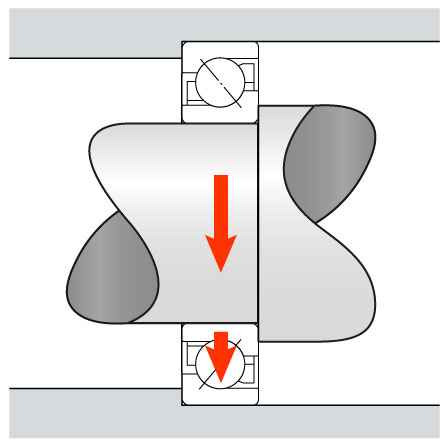
Radial Load
When the load is perpendicular to the shaft due to gravity.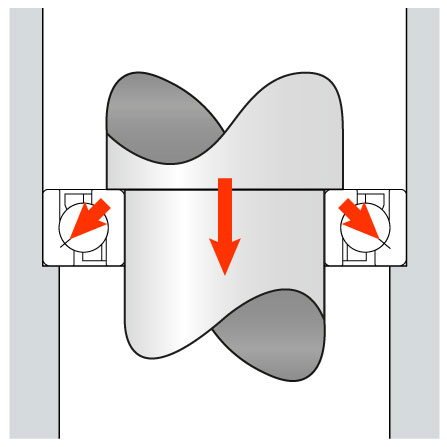
Axial or Thrust Load
When the load is parallel to the shaft - Axial load in a vertical pump or electric motor due to gravity.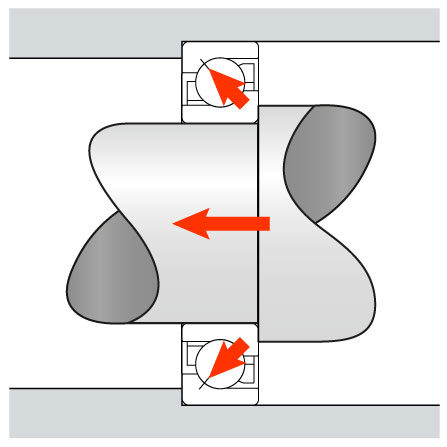
Axial or Thrust Load
When the load is parallel to the shaft - Axial load in a horizontal pump.(Ref.: www.skf.com)
